Global Inflation 2022: Has History Been Repeated This Time?
- Business
 Niccolo Romano
Niccolo Romano- June 14, 2022
- 0
- 22 minutes read
The global inflation 2022 portrays the effects of the pandemic related lockdowns in 2020 and also 2021. More recently, even though, it has been boosted by the increase in energy and food prices, mainly because of the Ukraine-Russia war that started in February 2022.
This crisis has injected major shocks into the markets of the community, disrupting global trends of production, trade, and consumption in ways that have chances to keep the prices at the high levels in the coming year.
As per the data portrayed on the global commodity market from March 2022, oil and wheat are at the present moment both nearly 50% more expensive in comparison to their prices a year ago. The values of other cereal grains are also increasing. For the importing nations, these rise in values offer a prominent hindrance to the economic growth and also livelihood, potentially increasing political and social tension.
Having said that, there is another factor that is directly proportional to inflation and that is the growth in GDP. Now this is a very important thing that you should understand. GPD (Gross Domestic Product) of a nation increases when the citizens earns more and spends more. Now as expenses rise along with the rise in GDP, inflation also rises. So if the governing bodies aim to decrease inflation, they will also decrease the GDP of the nation which is also not good. And if we look at this in this way, if the government tries to increase the GDP of a nation through its policies, then inflation will also rise as both are interconnected.
This article will serve as a case study for finding out how similar is this global inflation 2022 with the previous two big inflations in the history of economics.
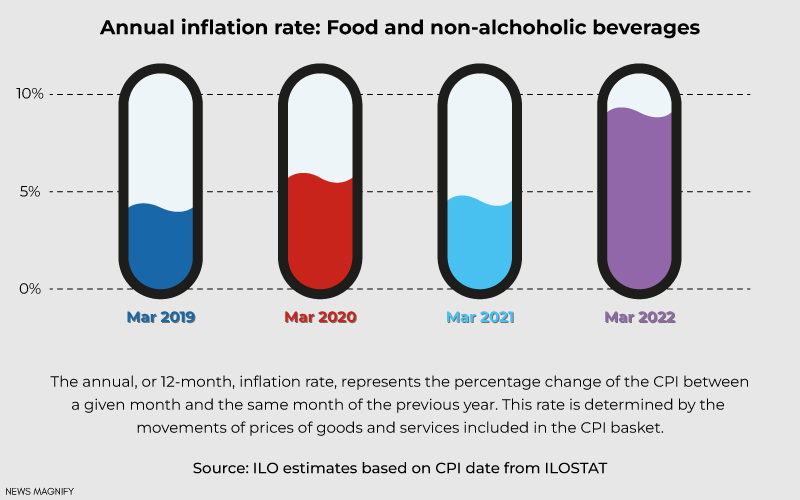
Global Inflation 2022: How Has It Become A Global Problem?
What caused this inflation to become stubbornly entrenched in nations across the globe is the invasion of Russia in Ukraine. Values increased the previous year on the back of the clogs of the supply chain, lockdown related to the Covid-19, and increasing energy charges. These were the issues that were anticipated to lessen in 2022.
Six months ago, the O.E.C.D (Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development) anticipated that hardly any of its 38 members would witness inflation rates increase above 9%. The primary exceptions included Argentina and Turkey, which were hardly struggling with runaway inflation mainly unassociated with the pandemic.
Since then, sanctions issued against Russia which is among the top energies in the world and a producer of grains, have supercharged food, fertilizer, and fuel prices. Russian bombing, seizures, and blockades have cut off the grain flow from Ukraine, which is another biggest producer, increasing the range of famine in the poorest food-importing countries.
At the same time, the policy of China of locking down areas where there are Covid-19 outbreaks has raised the issue. The previous week, the O.E.C.D declared sobering updates. In seven eastern European nations, the rate of inflation is presently expected to increase past double digits. The anticipated rates for the Netherlands this year tripled to 9.2%, and the inflation rate in Australia has doubled to 5.3%. And like the United States, where inflation increased 8.6% throughout May, Germany, and Britain have witnessed inflation rates hit four decade highs, well beyond previous anticipations.
This is likely to consume the income and savings of the households while impeding efforts by entities to invest and create jobs.
Central banks in the US, Australia, Britain, and India have all recently shifted aggressively to include rapidly increasing values by raising the rates of interest. Even the European Central Bank, which has been reluctant to increase rates for the fear of triggering a recession, stated that it would end asset buys and increase its key interest rates by a quarter point at its meeting the next month, and possibly by even more in this September.
But having said that there is a limit to what financial and political leaders can do regarding the increasing global inflation 2022, especially given the different causes. In many sections like Europe, inflation has been driven by prominent spikes in energy and food prices. Increasing rates will not solve the underlying supply issues, the O.E.C.D warned.
By contrast, the institution has partly blamed inflation in the US on “over-buoyant demand” which is more responsive to strengthening monetary policy. In comparison with Europe, the United States labor market is tighter and the nominal wage growth is higher.
Even though inflation is creating intense pain in some areas, the long term forecast is on the positive side. The World Bank anticipates the rate of global inflation 2022 to drop below 3% in the next year.
Global Inflation 2022: A Comparison With History
Let us see what history has to show us.
Global Inflation 2022: Is The History Of 1929 Repeated In 2022?
There are various similarities between what we are going through this year and what actually took place right prior to the starting of the Great Depression (financial) in 1929. However, what we are witnessing today would lead to a worsening scenario and it would call for urgent actions.
What Actually Happened In 1929?
The stock market lost nearly 80 percent of its value gradually between 1929 and 1932. In the first two weeks after the market crash of September 1929, it had already decreased by 40%. After short term fixing interventions from the FED to restrict the crisis, the crisis turned worse, longer, and global.
Factoring in the inflation, those who made investments in 1929 had to wait until 1992 for breaking the event on their investment.
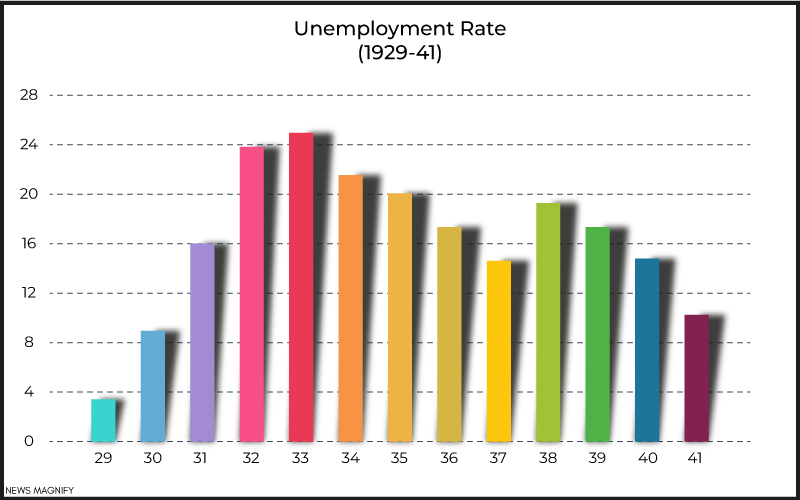
In 1928, which was the final year of the Roaring Twenties, the rate of unemployment was 4.2%. That is less than the natural rate of employment. By 1930, its rate increased more than double to 8.7%. By 1932, it had risen to 23.6%. This rate peaked in 1933, attaining up to nearly 25%. Nearly 15 million people lost their jobs. That is the highest rate of unemployment ever recorded in America.
Global Inflation 2022: How Similar Is It With The 2008 Inflation
In 2008, economists were found resolute by the Great Recession that followed the wake of the bankruptcy of the Lehman Brothers. The primary reason for this failure was that the company had turned a blind eye to the acute vulnerability of the financial sector to the potential bursting of the United State credit and housing market bubble. In this scenario, that bursting created a deep and painful economic recession.
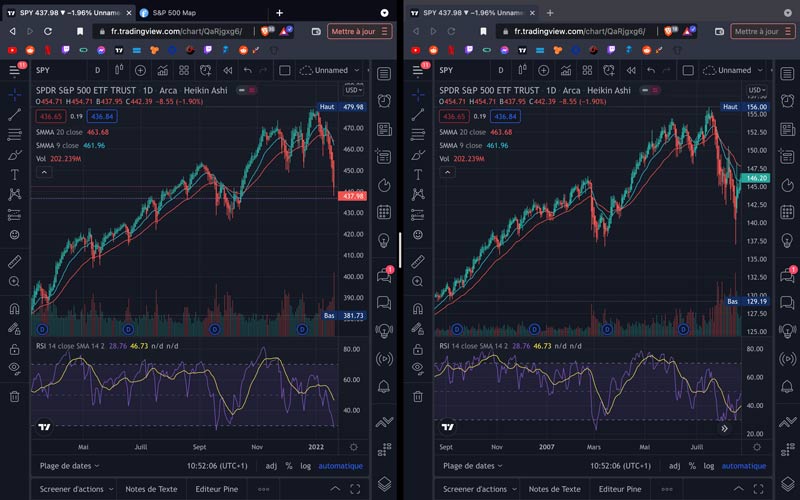
Today it looks like that many economists have learned little from their 2008 anticipating failure. Instead of emphasizing on how vulnerable the United States and the world economy 2022 financial mechanism are to the potential bursting of the global “everything” asset value and credit market bubble, many are talking about the risk of a return to the 1970s inflation issues. The chart below will tell you how similar both these S&P 500 Indexes looks.
What Can We Conclude From This Comparison?
We can start to witness parallels between the 1929-32 financial crisis, but there are prominent differences. The obvious difference is monetary, with the Dow being valued in gold ninety years ago, while in the present day it is completely fiat. But the value in gold, we can see from the below chart that the present day’s Dow hiked in April 2019.
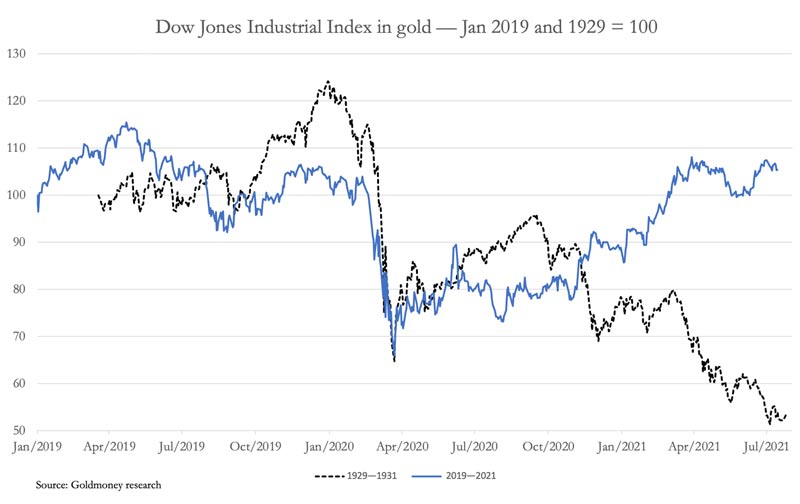
The experience of the previous financial crisis ninety years ago and its economic impact led to the gradual rejection of sound money and also the adoption of the present day policies informed by neo-Keynesian inflationism. It has ended up with the central banks, conducted by the Fed, directing monetary policy for creating a sustained wealth impact via asset value inflation. This policy was first identified by Alan Greenspan and has been accelerated by each crisis since, most renowned by Ben Bernanke dealing with the failure of Lehman Brothers.
This has been a long narrative, but thanks to the same crisis that occurred in France three centuries ago, we can start to discern the possible results of the prevailing monetary policies. Mixed with cyclical pressure, repeating the excesses of the valuation of the market witnessed in 1929, central banks have also created inflation of values which is now out of their control. The rates of interest are bound to increase soon, something that is already resisted strongly. The scenario for a crash in financial assets is falling into space and we can be sure that the monetary authorities will do anything to stop it. It is either this or they sit back and allow free markets to sort out the things themselves, for which they do not have any mandate.
When this happens, the order is likely to be initially an asset value crisis leading to sought widespread liquidation. It will be quickly followed by a collapse in the currency as the panic authorities try to sustain asset values. After all these, this can be a logic that we derive, assured by empirical evidence from the experience of John Law.
Global Inflation 2022: How To Fight Inflation?
Inflation takes place when spending on products and services exceeds production. Prices can increase as the supply constraints increase the costs of producing goods and providing services, or even because users enjoying the advantages of a booming industry, spend their extra cash quicker in comparison to the increase of production by producers. Inflation is often the outcome of some combination of these two instances. So, let us have a look at the steps taken by governments to control inflation in any economy.
1. Price Control
Price controls are price floors or caps mandated by the government and are applied to prominent items. Wage controls can be executed in teams along with price control for suppressing wage pull inflation.
In 1971, U.S. President Richard Nixon executed far attaining price controls in a try to counter increasing inflation. The price controls, though popular initially and are thought to be effective, failed to control prices when the inflation of 1973 skyrocketed to its highest levels since WWII.
Despite several intervening factors, most economists see the 1970s as proof enough that price controls are an impactful tool for handling inflation.
2. Contractionary Monetary Policy
Currently, contractionary monetary is a more famous method to control inflation. The aim of this policy to fight global inflation 2022 is to decrease the supply of money within an economy by raising interest rates. This helps to slow the growth of the economy but creates credit more expensive, which decreases user and business spending.
Higher rates of interest on government securities also make the growth slow by incentivizing investors and banks to purchase Treasuries, which assure a fixed rate of return, instead of riskier equity investments that get an advantage from the low rates. Now let us have a look at some of the tools via which the United States central bank, the Fed (Federal Reserve) fights inflation.
Federal Funds Rate
The Federal Fund Rate is the rate at which the banks lend each other money overnight. This rate is not set directly by the Fed. Instead, the FOMC announces a perfect range for the Federal Fund Rate and it then adjusts two other rates of interest, the IOR (Interest on Reserve) and ON RRP (Overnight Reverse Repurchase Agreement) to push the interbank rates into the perfect Fed fund range. This is done by other central banks as well and is a global phenomenon.
Open Market Operations
Reverse repurchase agreements are instances of open market operation (OMOs), which implies the purchasing and selling of Treasury securities. They are a tool with which the Fed raises or reduces the supply of money and adjusts the rates of interest.
Reserve Requirements
Up until March 26, 2020, the Fed also handled the supply of money via reserve requirements, or the percentage of money banks legally need to keep on hand for covering withdrawals. The more money banks were needed to hold back, the less they had to lend to the users.
Discount Rate
The discount rate is basically the interest rate levied on loans made by the central banks to the commercial banks and also other financial institutions. The lending facility via which these short-term loans are prepared is known as the discount window. The discount rate, which is similar across all the Reserve Banks across the globe, is created by consensus of each board of directors of regional banks and also the Board of Governors of the Fed.
Global Inflation 2022 By Startups Explained
There is no doubt that valuation for startup entities that include those in the areas of enterprise and technology has been broadly inflated lately. Now, as the market suffers a start-of-the-year swoon, these startup founders look to have another issue of inflation. This raised concerns about the impact of the fluctuation of the market and the possibility of a sustained downturn will be encountered by their businesses. The constant fluctuations of global businesses like Meta and PayPal whose shares fell last week and Google and Amazon whose shares went up, among others are bringing in ample confusion, but mostly tensions.
The Explanation
The latest market shift might lower the valuation of some of the private companies as of now, and potentially even delay some of the IPOs. But cloud and enterprise-tech companies are still commanding their valuation substantially greater than their long-term averages, boosted primarily by bigger picture technology and also the trends of the society that are propelling the annual incomes of several companies to $1 billion and beyond. Below is the analysis of the latest valuation trends for more than 100 software companies. It shows those companies being valued, as of Feb 2022, on average at just below 13 times forward revenues. This is down from just more than 23 times approximately a year ago, but it is still relatively in line with the average pre-pandemic Q1 2020.
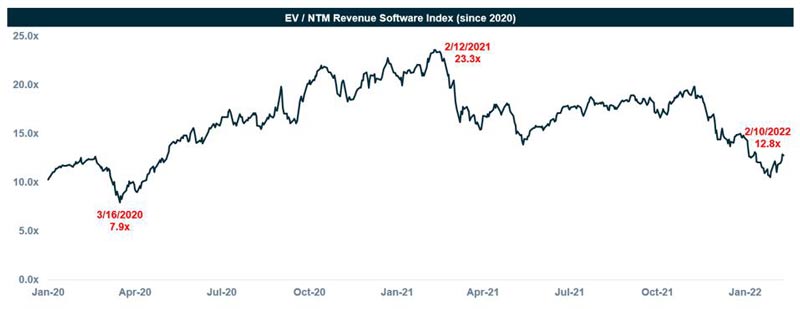
We realize that the market remains completely unpredictable. But there is only so much the founders can manage here and you are required to keep your eyes on the prize. Interest rates, Fed policy, and various Covid trends are beyond your power of influence. What can be controlled? A focus on your users, solving real life issues that digitally change the business of your users and beyond all using the likelihood of greater interest rates as a wake up reminder to utilize your capital more effectively for development.
Overall, despite the short term noise and vivid news coverage on the recent drive of the Nasdaq, we remain very bullish on the wider economic and software trends that are boosting businesses in association to cloud computing, artificial or data intelligence, and cybersecurity, among other industries. Here are the reasons why adapting your business for harnessing those trends and constructing entities of lasting value in the present scenario.
- Software prevails to transform just nearly every sector and you can harness it as well. Some call this prevailing trend “digital transformation.” But it really just implies that more companies, across sectors ranging from finance to manufacturing to healthcare to agriculture and others, are shifting to software for operating their businesses more effectively and serving customers.
- The overall IT spending and also the spending on the cloud-primarily prevails to develop. As per Gartner, overall technology spending is likely to develop at a 6% compound annual rate of growth from approximately $4.5 trillion currently.
- Aim at effective growth and spend the more expensive capital wisely. Given this, our advice is to aim at the users and if possible leverage more effective sales motions such as product led growth for qualifying your prospect and streamlining the process of sales.
Conclusion
What signs should we take about the future from the present global inflation 2022? There are many signs but not all are signs. To be sure, inflation in the current situation is running high and after keeping out the typically fluctuating categories of energy and food prices, is running higher in comparison to what it was for decades. But because of the features that are leading to this global inflation 2022 is a pandemic and also the Russia-Ukraine war that is still on. But before we end, here is a list of global inflation rates by countries 2022.
- Venezuela — 1198.0%
- Sudan — 340.0%
- Lebanon — 201.0%
- Syria — 139.0%
- Suriname — 63.3%
- Zimbabwe — 60.7%
- Argentina — 51.2%
- Turkey — 36.1%
- Iran — 35.2%
- Ethiopia — 33.0%
- Rwanda — -2.0%
- Chad — -0.5%
- Maldives — -0.2%
- Gabon — 0.6% (tie)
- Japan — 0.6% (tie)
- Bahrain — 0.7%
- Fiji — 0.8%
- Vanuatu — 0.9% (tie)
- Bolivia — 0.9% (tie)
- Saudi Arabia — 1.1%